- Super User
- 2023-04-11
Knowledge points for selection of cemented carbide materials for woodworking cut
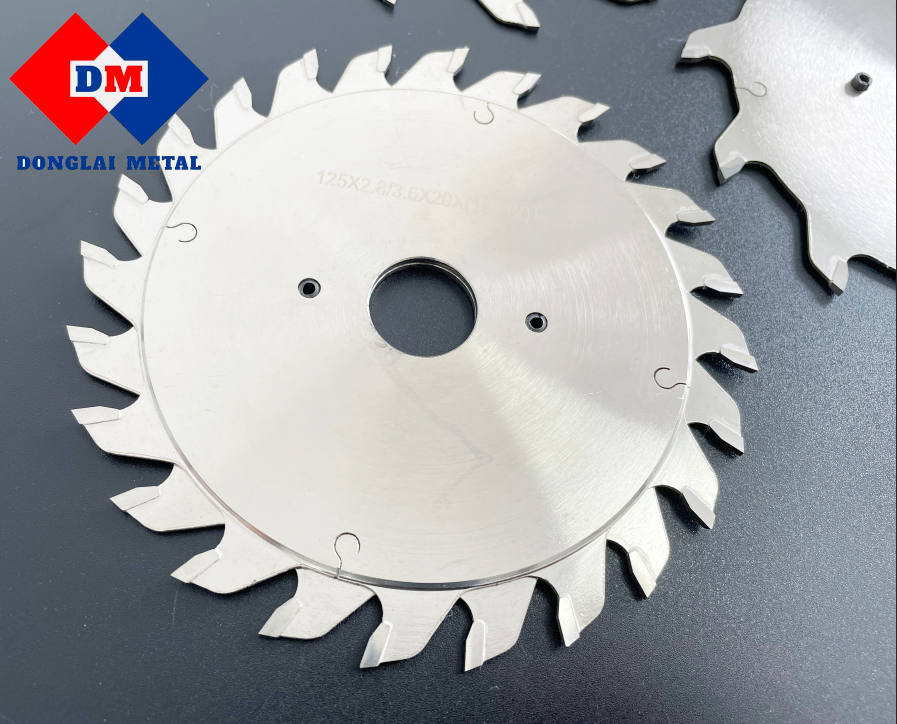

Carbide knives used in woodworking cutting have several subdivisions, such as circular saw blades, strip band saws, milling cutters, profiling knives, etc. Although there are many types of knives ,all kinds of knives are mainly selected according to the material and characteristics of cutting wood ,and the corresponding cemented carbiade for cutting different materials is listsd below. The following lists the cemented carbides corresponding to different material cutting.
1. Particle board, density board, and chipboard These boards are mainly artificially synthesized by wood, chemical glue, and melamine panels.Its characteristics are that the veneer is relatively hard ,the inner layer has a high glue content and there will be a certain proportion of hard impurities. During the cutting process, the furniture factory has strict requirements on the burr of the cutting section, so such wood boards usually choose cemented carbide with a Rockwell hardness of 93.5-95 degrees. The material of the alloy mainly chooses tungsten carbide with a grain size below 0.8 um and low content of binder phase. In recent years, due to the replacement and evolution of materials, many furniture factories have gradually selected composite diamond saw blades instead of carbide saw blades for cutting in panel electronic cutting saws. Composite diamond has higher hardness,and its adhesiveness and corrosion resistance are better tahn cemented carbide in the process of wood-based panel cutting . According to field cutting performance statistics , the service life of composite diamond saw blade is at least 15 times that of cemented carbiade saw blade.
2. Solid wood mainly refers to all kinds of native plant wood. The cutting difficulty of different planted wood is not the same. Most knife factories usually choose alloys with a degree of 91-93.5. For example, the knots of bamboo and wood are hard but the wood is simple, so alloys with a hardness above 93 degrees are usually selected to ensure better sharpness; logs with more knots are not uniformly stressed during cutting, so the blade It is very easy to cause chipping when encountering knots, so the alloy between 92-93 degrees is usually selected, which not only ensures a certain sharpness but also has a certain degree of collapse resistance, while wood with few knots and uniform wood ,alloys with a hardness above 93 degrees will be selected. As long as high wear resistance and sharpness are guaranteed, they can be cut for a long time; the original wood in the north will form frozen wood due to extreme cold in winter, and the frozen wood will increase the hardness of the wood. In addition, cutting frozen wood alloys in extremely cold environments is more prone to chipping, so in this case, alloys with a temperature of 88-90 degrees are usually selected for cutting.
3. Impurity wood. This type of wood has a lot of impurities. For example, the boards used in construction sites usually have high cement content, and the boards dismantled by furniture usually have gun nails or steel nails, so when the blade collides with hard objects during cutting It will cause chipping or broken edges, so cutting such wood usually chooses alloys with lower hardness and higher toughness. Such alloys usually choose tungsten carbide with medium and coarse grain size, and the content of binder phase is relatively high. The Rockwell hardness of such alloys is usually below 90. The selection of cemented carbide for woodworking cutting tools is not only based on the characteristics of cutting wood, but the tool factory usually also conducts comprehensive screening according to its own manufacturing process, furniture factory equipment and operating technology and other related conditions, and finally selects the cemented carbide with the best matching.